Cryptocurrency
Cryptocurrencies have revolutionized the world of finance by offering decentralized and secure digital alternatives to traditional fiat currencies. Since the emergence of Bitcoin in 2009, the cryptocurrency landscape has expanded significantly to include a diverse range of digital assets with unique features and applications.
- What is Cryptocurrency?
- History and Evolution of Cryptocurrencies
- Types of Cryptocurrencies
- Cryptocurrency Categories with Examples
- Bitcoin (BTC)
- Altcoins
- Stablecoins
- Meme Coins
- Utility Tokens
- DeFi Cryptocurrencies
- Governance Tokens
- Privacy Coins
- NFT-Related Tokens, Gaming Tokens, and Metaverse Tokens
- RWA Cryptocurrencies
- AI Cryptocurrencies
- Cryptocurrency Market Cap and Trends
- Top 10 Cryptocurrencies by Market Cap:
- The Cryptocurrency Market Regulatory Landscape
- The Future of Cryptocurrency
- How to Buy Cryptocurrency
- How to Buy Cryptocurrency - 5 Steps
- Staking or Interest Earning Options
- Cryptocurrency: Conclusion
What is Cryptocurrency?
Cryptocurrency is a type of digital or virtual currency that uses cryptographic techniques to secure transactions and regulate the creation of additional cryptocurrency units.
Unlike standard fiat currencies issued by central banks, cryptocurrencies operate on decentralized systems based on blockchain technology, a distributed ledger of data maintained by a network of computers (nodes). The principle of decentralization provides transparency, reduces the need for intermediaries, and increases the security of transactions.
History and Evolution of Cryptocurrencies
The theoretical concept of digital currency dates back to the late 20th century, but it wasn’t until 2009 that the first decentralized cryptocurrency, Bitcoin (BTC), was introduced by an anonymous person (or group of people) known online as Satoshi Nakamoto. Bitcoin was created in response to the global financial crisis of 2008-2009, with the goal of issuing BTC as an alternative to traditional banking systems.
Bitcoin’s success paved the way for thousands of alternative cryptocurrencies, each designed with unique functionality and application capabilities.
Types of Cryptocurrencies
Cryptocurrencies have diversified over the years, catering to different use cases and technological advances. The main categories include:
Cryptocurrency Categories with Examples |
|
| 1 |
Bitcoin (BTC)Bitcoin is humanity’s first cryptocurrency, often referred to as digital gold, serving as a store of value, investment, and medium of exchange. |
| 2 |
AltcoinsShort for “alternative coins,” these are any cryptocurrency other than Bitcoin. Their role and function are often aimed at addressing Bitcoin’s limitations or serving specific digital and economic niches. Notable examples of altcoins include:
|
| 3 |
StablecoinsStablecoins are cryptocurrencies that are pegged to stable assets, such as fiat currencies or commodities, to minimize price volatility. They are commonly used in trading and as a store of value. Here are a few examples:
|
| 4 |
Meme CoinsStarting as internet jokes or memes, these cryptocurrencies have gained popularity through community hype and speculative trading. Here are a few notable examples:
|
| 5 |
Utility TokensThese tokens provide holders with access to certain products or services in the blockchain ecosystem. They are integral to the functioning of many platforms. Here are a few examples:
|
| 6 |
DeFi CryptocurrenciesDeFi (Decentralized Finance) cryptocurrencies provide decentralized financial services such as lending, borrowing, and yield farming without intermediaries. Here are some examples of DeFi cryptocurrencies:
|
| 7 |
Governance TokensGovernance tokens (cryptocurrencies) provide voting rights in decentralized protocols, allowing their holders to influence the development and governance of blockchain projects. Here are some examples:
|
| 8 |
Privacy CoinsDesigned to enhance the anonymity of transactions, these cryptocurrencies hide the identity of the sender and receiver. Here are some well-known examples:
|
| 9 |
NFT-Related Tokens, Gaming Tokens, and Metaverse TokensGaming tokens and metaverse tokens are cryptocurrencies associated with blockchain-based virtual worlds and games. NFT tokens facilitate the purchase, sale, and creation of non-fungible tokens (NFTs) on blockchain-based marketplaces. Here are some examples:
|
| 10 |
RWA CryptocurrenciesReal-World Asset (RWA) cryptocurrencies are digital tokens that represent digitized ownership of physical assets such as real estate, commodities, or bonds. The goal of issuing such tokens is to combine traditional finance with blockchain technology, increasing the liquidity and accessibility of real-world investments. Examples of RWA cryptocurrencies include tokenized gold like PAXG and real estate-backed tokens on platforms like RealT. |
| 11 |
AI CryptocurrenciesAI-powered cryptocurrencies use artificial intelligence to enhance blockchain-based applications, such as predictive analytics services, automated trading functionality, and decentralized AI services. These projects integrate AI models to optimize blockchain networks, analyze market trends, or provide financial services based on AI capabilities. Notable examples include:
|
Cryptocurrency Market Cap and Trends
The cryptocurrency market has seen exponential growth over the past decade. From a total market cap of just over $1.5 billion in 2013, it has grown to over $2 trillion by 2021, and surpassed $3.8 trillion in 2025. This growth reflects growing institutional adoption, technological advances, and broader public interest.
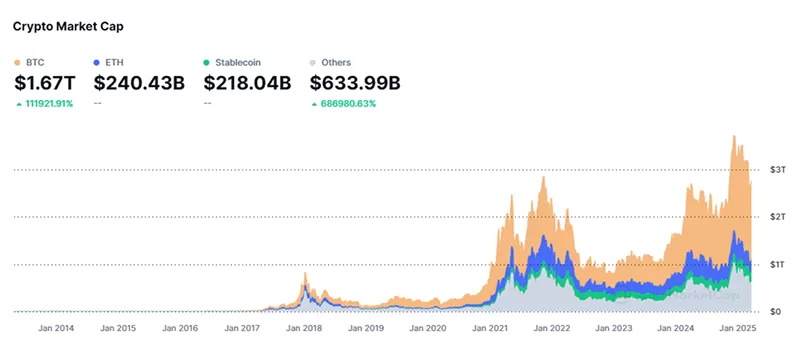
Individual cryptocurrencies have also experienced significant fluctuations in market cap. For example, Bitcoin’s market cap has grown from around $1 billion in 2013 to over $1 trillion in 2021, and surpassed $2 trillion in 2025. Ethereum has followed a similar trajectory, but it reached a market cap of over $560 billion in 2021 and has yet to surpass it as of March 20, 2025.
Top 10 Cryptocurrencies by Market Cap:
| № |
Cryptocurrency (Ticker) |
Market Capitalization (in billions of dollars) | Share of Total Capitalization (%) |
| 1 | Bitcoin (BTC) | 1 670,82 | 60,5 |
| 2 | Ethereum (ETH) | 240,61 | 8,7 |
| 3 | Tether (USDT) | 143,44 | 5,2 |
| 4 | XRP (XRP) | 139,23 | 5,0 |
| 5 | Binance Coin (BNB) | 89,44 | 3,2 |
| 6 | Solana (SOL) | 66,45 | 2,4 |
| 7 | USD Coin (USDC) | 59,65 | 2,2 |
| 8 | Dogecoin (DOGE) | 25,05 | 0,9 |
| 9 | Cardano (ADA) | 25,00 | 0,9 |
| 10 | TRON (TRX) | 22,28 | 0,8 |
The total capitalization of these 10 cryptocurrencies as of 03/22/2025 is $2,481.97 billion US dollars, which is equivalent to 89.9% of the total crypto market capitalization. The remaining 10.1% ($278.03 billion) is accounted for by the remaining 10,488 cryptocurrencies (the number of coins on the market as of 03/22/2025).
The Cryptocurrency Market Regulatory Landscape
As cryptocurrencies have become more visible, they have attracted the attention of regulators around the world. Different countries have taken different approaches, from embracing digital assets to imposing strict regulations or outright bans. The evolving regulatory environment aims to address concerns such as consumer protection, financial stability, and the prevention of illegal activity.
The Future of Cryptocurrency
The future of cryptocurrency remains a topic of active discussion. Possible promising developments include:
- Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs): Traditional financial institutions are exploring digital versions of fiat currencies to combine the benefits of cryptocurrencies with the stability of traditional money.
- Integration with Traditional Finance: As economic adoption increases, cryptocurrencies may become more integrated into traditional financial systems, offering new investment opportunities and financial products.
- Technological Innovation: Advances in blockchain technology could lead to increased scalability, reduced energy consumption, and broader applications beyond finance, such as supply chain management and healthcare.
How to Buy Cryptocurrency
It is not difficult to buy cryptocurrency and is available to everyone. The procedure includes choosing a platform (exchange, etc.), registering an account and actually making a purchase. Below is a 5-step guide to help new investors make their first investment in cryptocurrency:
How to Buy Cryptocurrency - 5 Steps |
|
1. Choosing a Cryptocurrency Exchange The most common way to buy cryptocurrency is to do it on an online exchange. Popular cryptocurrency exchanges such as Binance, Coinbase, Kraken, Bybit and others offer various digital assets, competitive fees and all the necessary levels of account and transaction protection. |
|
2. Register and Confirm Your Account Register on the exchange by providing your email address, other required data and creating a strong password. Most exchanges require user identity verification (KYC) by providing the service with a government-issued ID and confirming your address using one of the suggested methods. |
|
3. Depositing Funds into an Account Fund your exchange deposit using fiat (regular) currency (USD, EUR, etc.) via bank transfer, credit/debit card, PayPal, or other payment methods supported by the exchange. Some exchanges also allow direct cryptocurrency deposits. |
|
4. Selecting the Desired Cryptocurrency and Making a Purchase Go to the trading section (you need Spot - spot trading), select a cryptocurrency (for example, Bitcoin, Ethereum or another) and specify the amount you want to buy. You can place a market order to buy (instant purchase at the current price) or a limit order (which will be executed by the exchange algorithm when the price reaches the desired one, set by you in the order). |
|
5. Storing Purchased Cryptocurrency Once you have purchased cryptocurrency, you can either store it on an exchange or transfer the tokens to a personal wallet for added security. Hardware wallets (such as Ledger and Trezor) provide the highest level of protection. |
Understanding these steps to buying digital coins will help new investors make informed decisions when entering the cryptocurrency market.
Staking or Interest Earning Options
Many cryptocurrency exchanges offer staking or other forms of earning income from the cryptocurrency you hold, allowing users to earn passive income from their holdings.
Cryptocurrency: Conclusion
Cryptocurrencies have already managed to change the global financial landscape by introducing decentralized, secure, and efficient means of value transfer. As the digital money ecosystem continues to evolve, it presents both opportunities and challenges, the development and resolution of which will shape the future of digital finance.